How Ethereum Verifies Transactions Using Only a Bitcoin Address
Asymmetric cryptosystems, such as those used in Bitcoin, rely on mathematical algorithms to verify transactions and ensure secure online transactions. One of the key features that distinguishes asymmetric systems from others is the use of a public key instead of a private key to sign messages.
In this article, we will explore how the Ethereum smart contract platform uses a combination of techniques to verify transactions without relying on a public key. Specifically, we will examine the role of Bitcoin addresses in the Ethereum transaction verification process.
Asymmetric Cryptosystems 101
When you generate an asymmetric pair consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key, an individual user keeps both of them secret. The private key is used to sign digital signatures, while the public key serves as a “fingerprint” or unique identifier for that private key.
The security benefits of this approach include:
- Private Key Protection: Private keys cannot be shared publicly, which helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive financial information.
- Digital Signature Verification
: The public key can be used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital signatures, ensuring that they were generated by the intended owner.
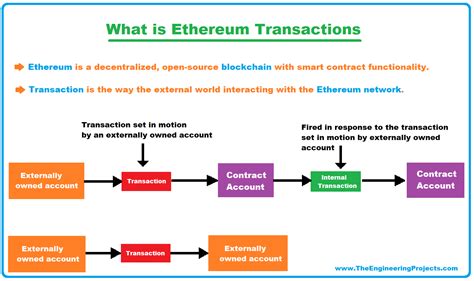
Ethereum Smart Contract Platform
When creating smart contracts on Ethereum, developers rely on a complex system that includes several cryptographic methods. However, Ethereum essentially uses Bitcoin addresses as an alternative to private keys to verify transactions.
Here are some key points about how Ethereum verifies transactions using only a Bitcoin address:
- Bitcoin Address: An Ethereum user generates a unique Bitcoin address that is used as a “signature” for their transactions.
- Transaction Hash
: When a transaction is transmitted over the network, its entire history is stored in a database called the blockchain. The transaction hash is calculated, and this value serves as a unique identifier for that transaction.
- Signature verification: Each Bitcoin address is associated with a corresponding public key. In Ethereum, the sender of a transaction uses their private key (secret) to create a digital signature using the Bitcoin address as a “fingerprint”. This process is called “signature verification”.
- Transaction verification: Once a transaction is verified, the following steps are performed:
- The blockchain database stores the transaction hash.
- Each participating party (e.g. miners, validators, and users) calculates their own signature using the public key associated with the Bitcoin address.
- The resulting signatures are compared to expected signatures generated by each node in the network. If the signatures match, the transaction is considered verified.
Key Benefits
Using Bitcoin addresses to verify transactions offers several benefits:
- Reduced private key risk: Since private keys remain secret, users don’t have to worry about sharing sensitive information.
- Enhanced security: The use of public keys and digital signatures helps prevent unauthorized access to financial transactions.
- Enhanced transparency: Blockchain databases store the entire transaction history for each Bitcoin address, providing a clear record of all activity.
Finally, the Ethereum smart contract platform relies on Bitcoin addresses as an alternative to private keys for verifying transactions. Using this approach, developers can create secure, decentralized systems that protect user data and enable trustless transactions without relying on traditional asymmetric cryptography methods.